The Lodgepole Pine Tree: A Pillar of the Wilderness
Welcome, young adventurers, to the world of the Lodgepole Pine tree, scientifically known as Pinus contorta. This resilient conifer is a key species in the forests of western North America. With its slender profile and adaptability to various environments, the Lodgepole Pine is not just a tree; it’s a crucial component of its ecosystem, known for its role in forest regeneration, especially after fires. Let’s explore the remarkable features and ecological importance of this hardy tree.
Characteristics of the Lodgepole Pine
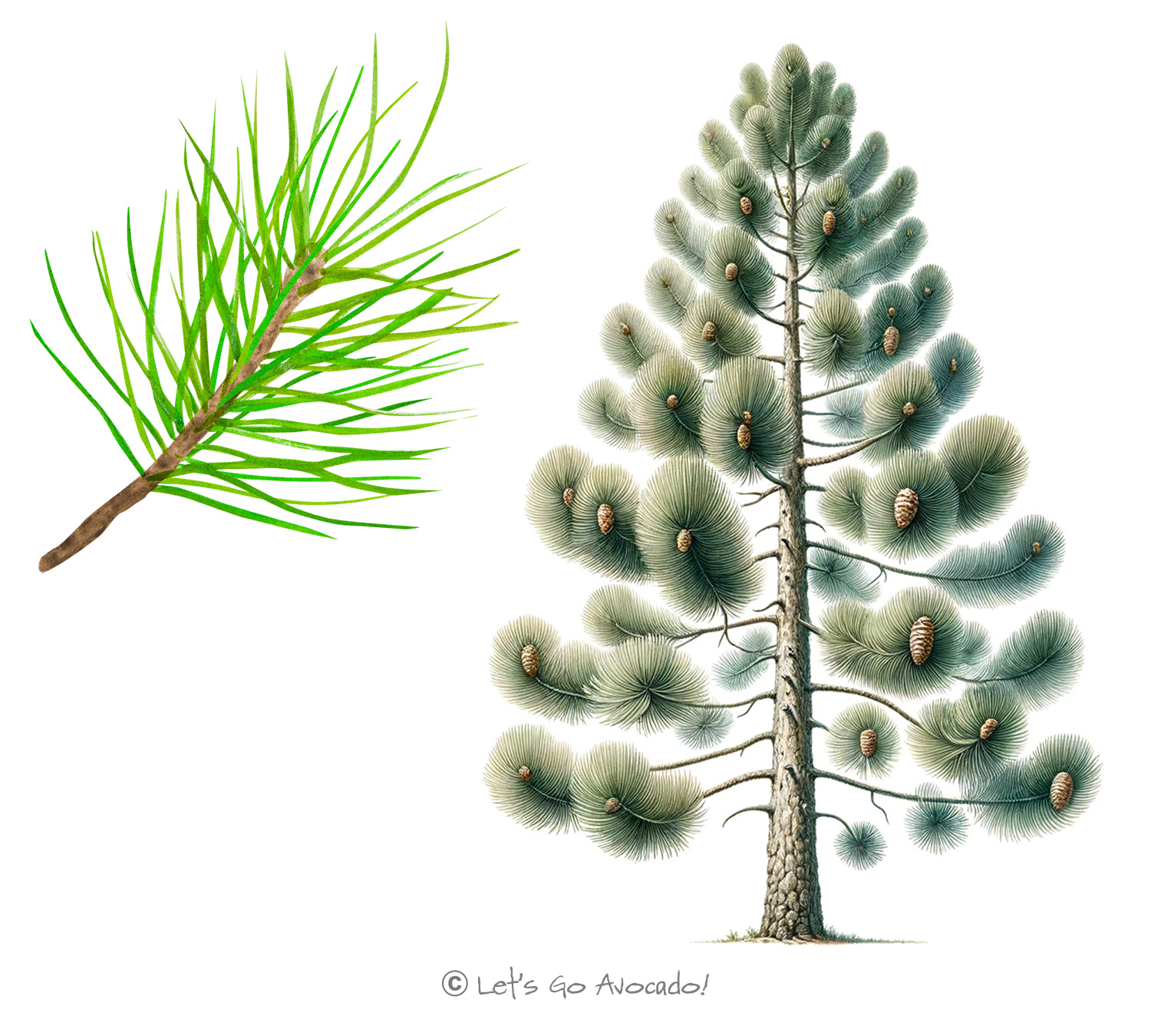
The Lodgepole Pine is recognized for its tall, straight growth and thin, flexible trunk. Its needles are bundled in pairs, short and often twisted, with a bright green color that stands out in the forest landscape. The tree produces cones that are uniquely adapted to their environment – some are serotinous, requiring the heat from a fire to open and release their seeds.
Size and Growth Habits
Typically, Lodgepole Pines grow to about 70-80 feet (21-24 meters) tall, although they can reach greater heights under the right conditions. Their growth pattern is largely influenced by the environment, leading to variations in form. In denser forests, they grow straight and tall, while in open areas, they may develop a more branched and spreading habit.
Lifecycle: Adapted to Fire
The life cycle of the Lodgepole Pine is closely tied to fire. The heat from forest fires causes the serotinous cones to open, releasing seeds onto the nutrient-rich soil. This adaptationAn animal adaptation is a physical feature or a specific behavior that allows it to better survive in its environment. allows the Lodgepole Pine to quickly colonize areas after a fire, playing a vital role in the regeneration of the forest.
Ecological Contributions
In its natural habitat, the Lodgepole Pine is essential for maintaining the health and balance of the forest ecosystem. Its ability to grow in poor soil conditions and to regenerate quickly after disturbances contributes to soil stabilization and habitat creation for a variety of wildlife species.
Resilience and Environmental Interactions
The Lodgepole Pine’s resilience is one of its most notable characteristics. It thrives in harsh conditions, from high altitudes to sandy soils, demonstrating a remarkable ability to adapt and endure in challenging environments.
Human Use and Appreciation
Humans have utilized the Lodgepole Pine in various ways. Its wood is valued for its versatility, used in construction, and as a source of pulp for paper production. The tree’s ability to grow quickly and in diverse conditions has also made it a popular choice for reforestation projects.
The Lodgepole Pine tree, with its unique adaptations and ecological significance, is an integral part of the forest landscape. As we explore the wilderness and encounter these trees, let’s appreciate their role in the natural cycle of growth and regeneration. The Lodgepole Pine is a key player in maintaining the health and diversity of forests, providing habitat for wildlife, and contributing to the overall beauty of the natural world.
As you continue your journey through nature, take the time to observe the Lodgepole Pines and their role in the forest ecosystem. Keep exploring and learning, and you’ll uncover the many roles and stories that trees like the Lodgepole Pine have to share.