The Honey Locust Tree: A Unique and Versatile Member of the Forest
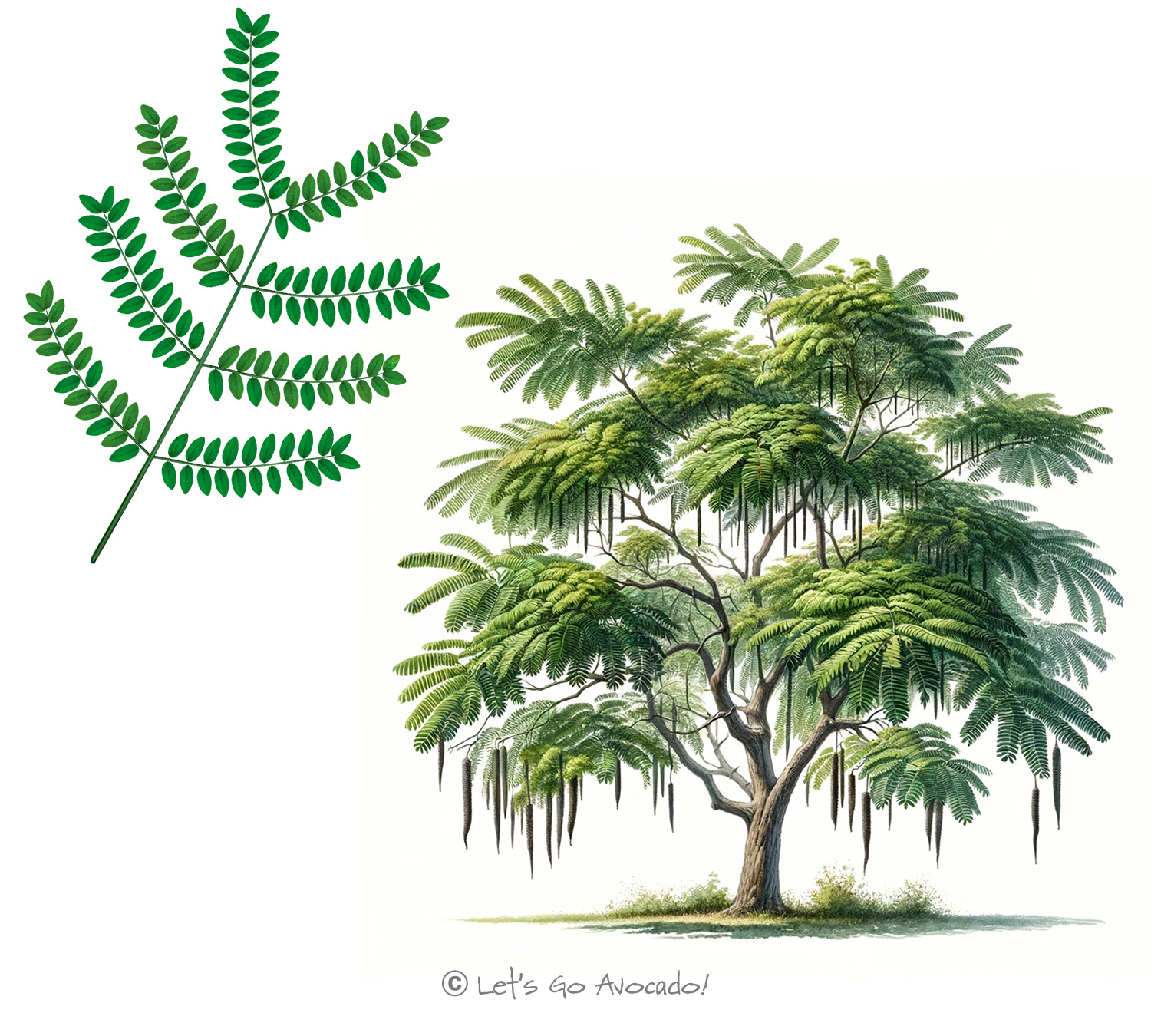
Welcome to the intriguing world of the Honey Locust tree, scientifically named Gleditsia triacanthos. This tree, easily identifiable by its distinctive thorns and feathery leaves, is a common sight in many parts of North America. The Honey Locust stands out not only for its physical characteristics but also for its adaptability and ecological importance. Let’s explore the remarkable traits and contributions of this versatile tree.
Identifying the Honey Locust
The Honey Locust is most notable for its long, sharp thorns that can grow on the trunk and branches. These thorns were once a defense mechanism against large grazing animals of the past. The tree’s leaves are small and delicate, forming a light, feathery canopy. In the fall, the tree produces long, flat seed pods that are often eaten by wildlife.
Size and Structure: Adaptable Growth
Honey Locusts can vary greatly in size, typically reaching heights of 60-100 feet (18-30 meters). They have an open, spreading canopy that allows light to filter through, making them a popular choice in both rural and urban landscapes. This adaptability in size and form allows Honey Locusts to thrive in a variety of settings.
Growth and Lifecycle: Rapid and Resilient
The Honey Locust has a fast growth rate, making it a popular choice for quickly establishing shade. Its seed pods, which contain the tree’s seeds, are an important food source for wildlife and play a key role in the tree’s reproductive process. The tree’s ability to grow in challenging environments, including urban areas, speaks to its resilience.
Ecological Contributions: More Than Just Shade
In its natural environment, the Honey Locust plays a significant role. Its canopy provides habitat for various bird species, and the seed pods are a food source for mammals. The tree is also used in agroforestry practices, as its leaves add nitrogen to the soil, improving fertility.
Challenges and Adaptations
While generally robust, the Honey Locust can be susceptible to pests and diseases. However, its fast growth and ability to adapt to different soil and climate conditions have made it a resilient species capable of withstanding various environmental stresses.
Human Use and Value
The Honey Locust has found various uses among humans. Its wood is strong and durable, used for posts, furniture, and sometimes firewood. The tree is also valued for ornamental purposes due to its unique appearance and the light shade it provides, making it a common sight in parks and streetscapes.
The Honey Locust tree, with its distinctive thorns, feathery foliage, and versatile nature, is a valuable addition to both natural and urban landscapes.
Every tree in our environment, including the Honey Locust, has its unique story and role. These stories enrich our understanding of the natural world and its intricate web of life. Continue exploring and learning, and you’ll discover the fascinating narratives of trees and their place in our world.