The Eastern Cottonwood Tree: A Giant Among Nature
Prepare to embark on an exploration of the Eastern Cottonwood tree, known scientifically as Populus deltoides. This impressive tree is a giant of the North American landscapes, especially along rivers and streams. Found predominantly in the eastern and central regions of the United States, the Eastern Cottonwood is known for its rapid growth and towering presence. It plays a significant role in its environment, providing essential benefits to both the ecosystem and the species that inhabit it. Join us as we delve into the captivating world of the Eastern Cottonwood tree.
Recognizing the Eastern Cottonwood
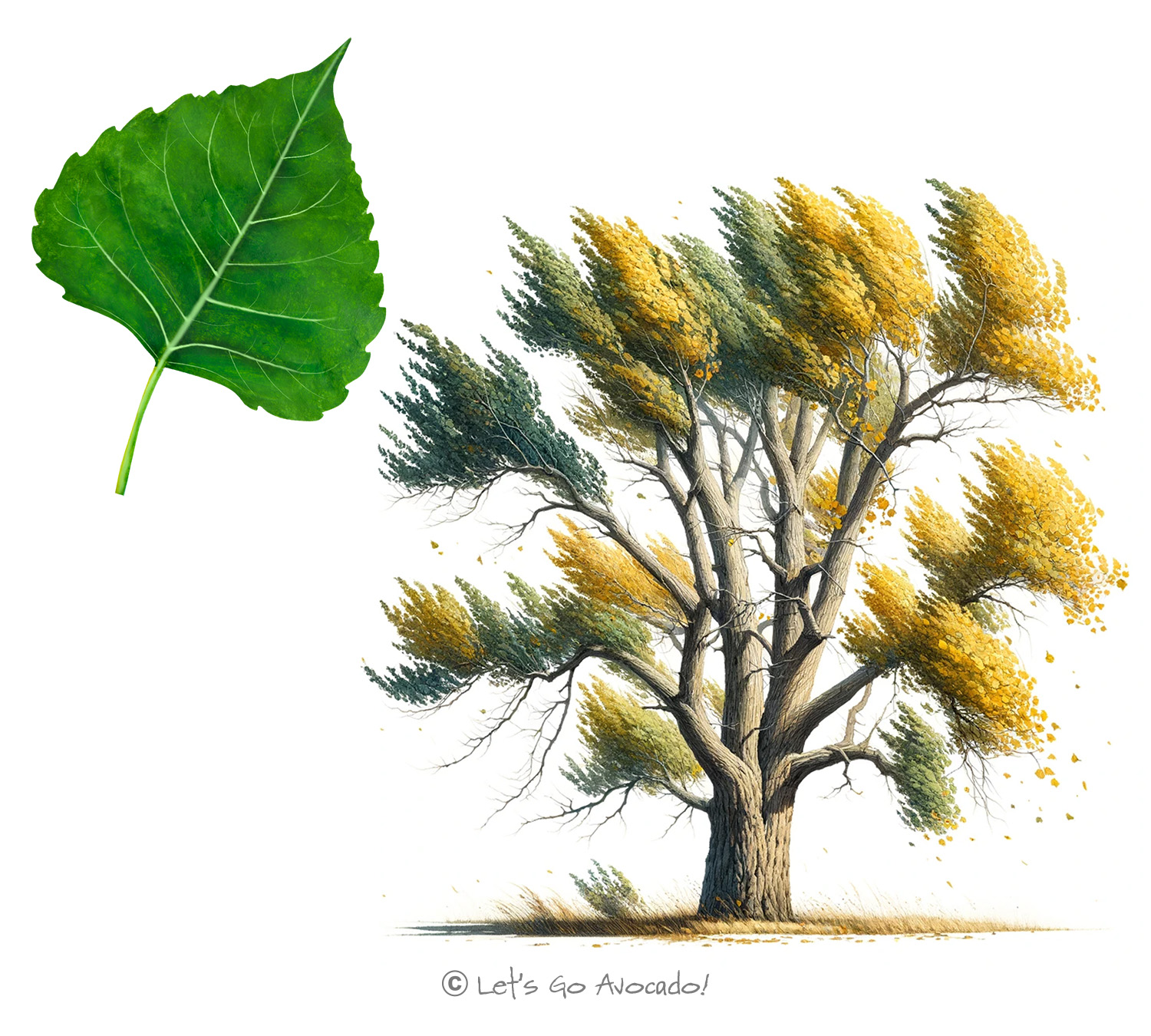
The Eastern Cottonwood is easily identifiable by its towering height and broad, open crown. Its leaves are uniquely shaped – broad and triangular, known for their fluttering in the slightest breeze. In the spring, the tree blooms with long, drooping catkins, followed by the appearance of its namesake cotton-like seeds, which float through the air in summer, creating a whimsical scene.
Size and Growth: A Rapidly Growing Giant
One of the most striking aspects of the Eastern Cottonwood is its size. These trees can grow to an astounding 100 feet tall (30 meters) or more, making them one of the tallest species in North America. Their rapid growth rate is another notable feature, enabling them to quickly dominate riverbanks and open areas.
The Lifecycle of the Eastern Cottonwood
The life cycle of the Eastern Cottonwood is as dynamic as the tree itself. After the flowering period, the tree produces seeds encased in a fluffy, cotton-like substance, aiding their dispersal by wind and water. The tree thrives in sunny areas with moist, fertile soil, often found along waterways where it plays a crucial role in stabilizing banks and supporting local ecosystems.
Ecosystem Contributions: A Keystone Species
In its natural habitat, the Eastern Cottonwood is a keystone species. Its dense foliage provides shelter and nesting sites for birds, while its presence along waterways helps prevent soil erosion. The tree also supports various wildlife species through its seeds and leaves, which serve as food sources.
Adaptability and Resilience
The Eastern Cottonwood, despite its size, faces challenges from pests and diseases. However, its ability to grow rapidly in favorable conditions demonstrates its resilience and adaptability, allowing it to maintain its presence in the landscape.
Human Use and Significance
Humans have long valued the Eastern Cottonwood for various purposes. Its wood is used in the manufacture of paper and crates, while its quick growth makes it useful for reforestation projects. The tree’s majestic presence also makes it a popular choice for landscaping in large open spaces.
The Eastern Cottonwood tree, with its impressive size and rapid growth, is a true marvel of nature. As it stands tall along rivers and landscapes, it not only adds beauty but also plays a vital role in supporting the environment.
Remember, each tree, including the Eastern Cottonwood, has its own story and role in the environment. These stories are important to our understanding and appreciation of the natural world. Keep exploring, and you’ll discover the endless wonders and roles of trees in our ecosystems.