Morel Mushroom
Morchella, sponge mushroom
Morchella
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
The morel mushroom is one of the most sought-after wild mushrooms in the world, known for its distinct appearance and exquisite taste. Every spring, foragers venture into forests in pursuit of these elusive fungi, and they are highly prized in culinary circles for their rich flavor and unique texture.
Morel Mushroom
Common Name
Morel Mushroom
Other Names
Morchella, sponge mushroom
Latin Name
Morchella
Distribution
Morels can be found in various parts of North America, Europe, Asia, and other continents. They primarily grow in temperateTemperate refers to a climate that’s not too hot and not too cold, with moderate rainfall and distinct seasons like spring, summer, fall, and winter. You’ll find temperate areas in parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. It’s the kind of climate where you can see a wide variety of plants and animals, including deciduous trees that lose their leaves in the fall. forests, especially in areas that have experienced recent fires.
Appearance
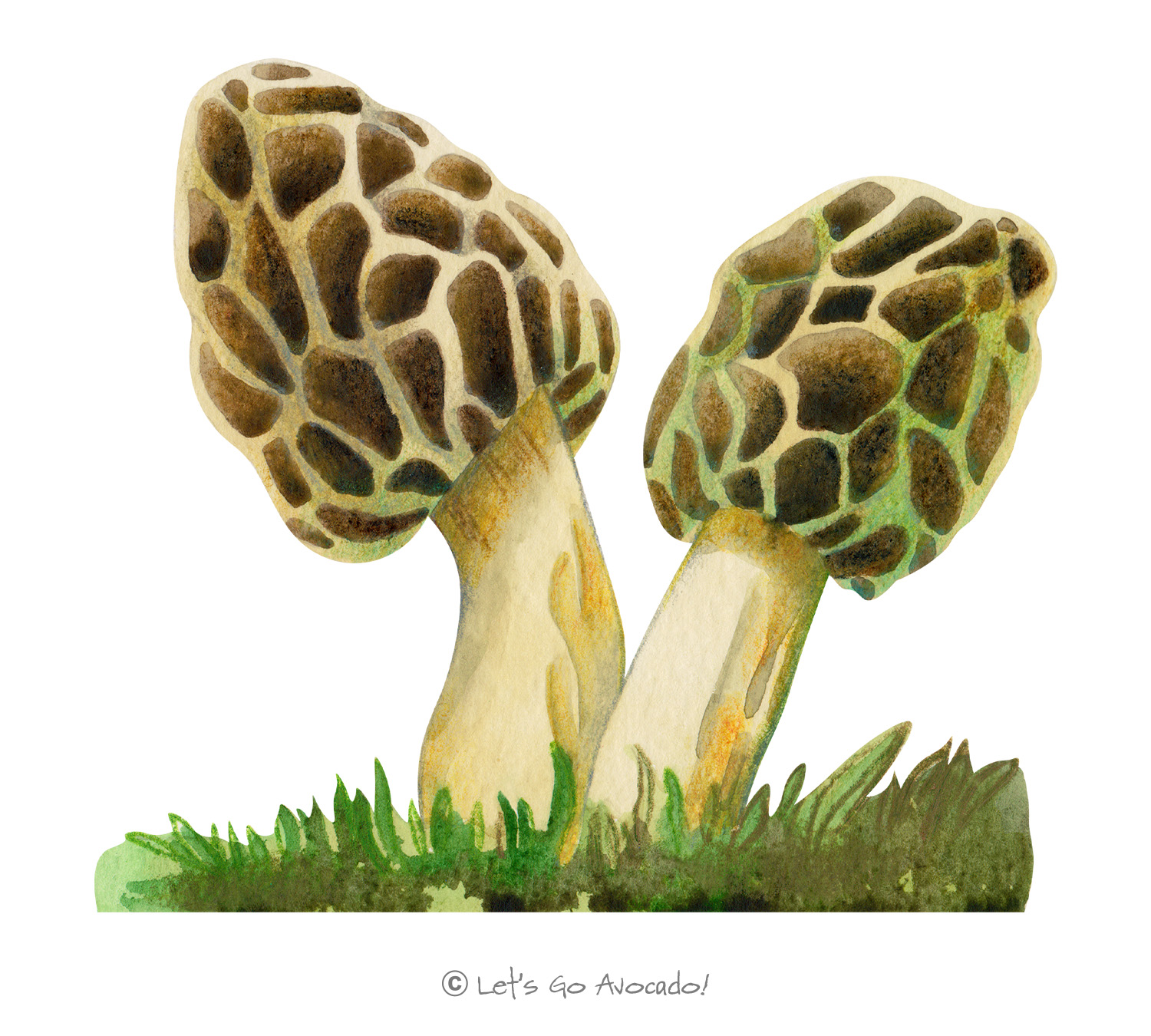
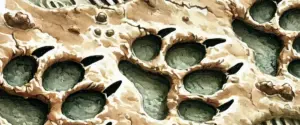
Morels have a honeycomb appearance due to the network of ridges and pits on their elongated caps. They are hollow from the tip of the cap down through the stem.
Size
Typically 5 to 20 cm in height, but this can vary based on the specific species and environmental conditions.
Habitat
Morels are often found in woodlands, particularly near ash, oak, elm, and apple trees. They can also thrive in areas recently affected by wildfires or other disturbances.
Diet
Morels are saprotrophic, meaning they derive nutrients from decaying organic matter. However, some believe they might also form mutualistic relationships with certain trees, absorbing sugars from the tree and providing minerals in return.
Lifecycle
Like other fungi, morels start as spores that germinate into a network of myceliumMycelium is like the ‘root’ or the ‘body’ of a fungus. Just as plants have roots, fungi have mycelium. It is made up of tiny thread-like structures called hyphae that spread out in the soil or other materials where the fungus grows. Learn More. Under suitable conditions, this mycelium forms the fruiting body we recognize as the morel mushroom. Once mature, the mushroom releases spores to propagate.
Defense Mechanisms
Morels contain small amounts of hydrazine toxins, which can cause stomach upset in some individuals if consumed raw. Cooking typically breaks down these toxins. It’s crucial to distinguish true morels from toxic false morels. Always consult an expert when foraging for wild mushrooms.
Ecological Importance
As decomposers, morels help break down dead organic material, recycling nutrients back into the soil. This aids in soil fertility and overall ecosystemAn ecosystem is a community of living organisms, like insects and birds, and non-living components, like water and rocks, that interact with each other in a specific area. Learn More health.
ConservationThe act of protecting and preserving natural resources and the environment. Conservation efforts are important to protect beavers and their habitats. Status
Morels are not easy to find, contributing to their allure among foragers. Overharvesting can be a concern in certain areas.

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.