Honey Mushroom
Armillaria, Shoestring Fungus, Bootlace Fungus
Armillaria mellea
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
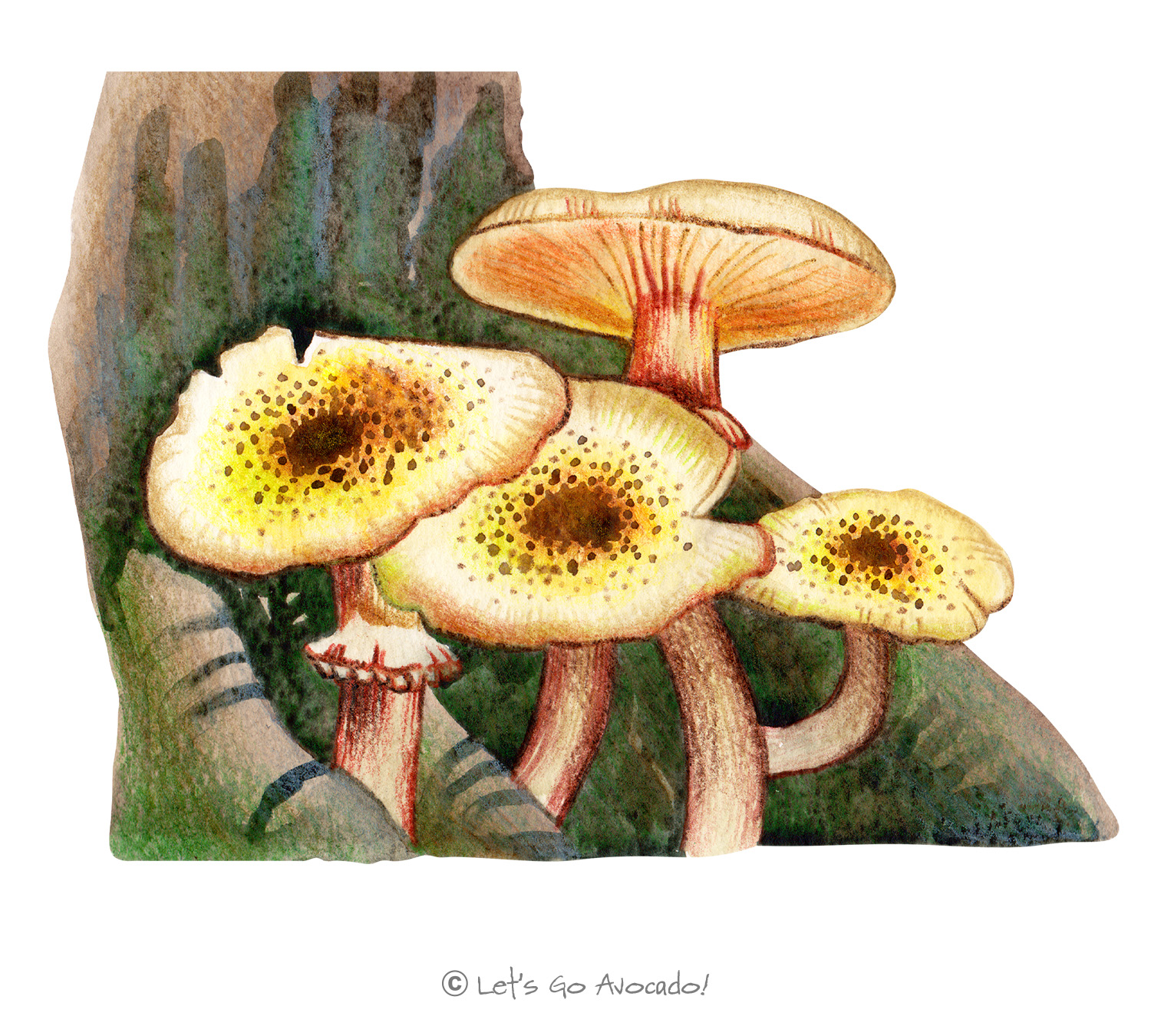
The honey mushroom is a woodland fungus known for its ability to colonize and kill a variety of trees and woody shrubs. This genus is particularly interesting because of the armillaria root rot it causes in forests, leading to large rings or arcs of dead trees in the affected areas.
Honey Mushroom
Common Name
Honey Mushroom
Other Names
Armillaria, Shoestring Fungus, Bootlace Fungus
Latin Name
Armillaria mellea
Distribution
Honey mushrooms have a wide distribution and can be found in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia.
Appearance
They usually have a yellow-brown cap that’s sticky when moist. The gills are white and sometimes produce a whitish spore print. One distinctive feature is the presence of a white, net-like pattern on the stem near the cap.
Size
The cap diameter ranges from 3 to 15 cm, and the stem can be between 8 to 20 cm tall.
Habitat
Honey mushrooms are primarily wood-decay fungi, thriving on hardwoods and conifers, often at the base of trees or on stumps and logs.
Diet
They are parasitic and saprotrophic, meaning they can extract nutrients from living trees as well as decomposeDecomposition is a natural process that happens when living things, like plants, animals, or other organic matter, break down into simpler substances. It is a part of the circle of life and plays an essential role in recycling nutrients back into the environment. Learn More dead wood.
Lifecycle
Beginning as spores, they grow as myceliumMycelium is like the ‘root’ or the ‘body’ of a fungus. Just as plants have roots, fungi have mycelium. It is made up of tiny thread-like structures called hyphae that spread out in the soil or other materials where the fungus grows. Learn More, colonizing wood. Once matured, the mycelium produces fruiting bodies (the visible mushrooms). These mushrooms then release spores, and the cycle continues. Their rhizomorphs (root-like structures) help them spread and infect trees.
Defense Mechanisms
The honey mushroom doesn’t have specific defenses against predators, but it’s worth noting that while many consider them edible, they can cause adverse reactions in some individuals. Proper cooking is advised, and they should never be consumed raw. Always ensure accurate identification before consumption.
Ecological Importance
While they play a significant role in decomposing dead wood, honey mushrooms can also be problematic due to the tree diseases they cause. They have both detrimental effects in forests and beneficial effects in recycling nutrients.
ConservationThe act of protecting and preserving natural resources and the environment. Conservation efforts are important to protect beavers and their habitats. Status
They are common and not considered threatened.

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.