Earthstar Gaestrum
Geastrum
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
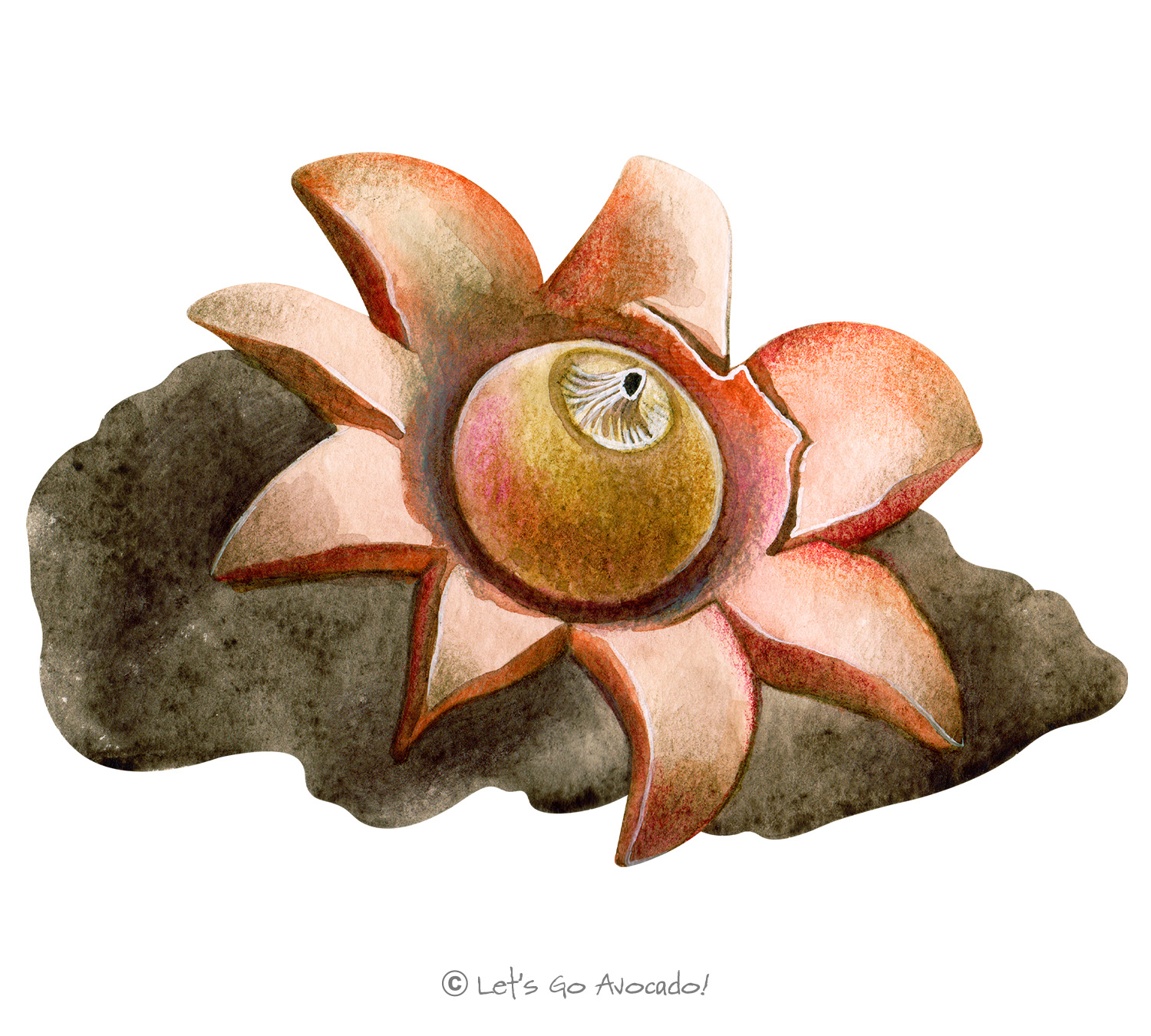
Earthstars, belonging to the genus Geastrum, are aptly named for their star-like appearance when their outer layer splits and peels back, forming pointed “arms” that resemble a star. These unique structures are puffballs, releasing their spores when they’re pressed upon by, for example, falling raindrops.
Earthstar Gaestrum
Common Name
Earthstar Gaestrum
Latin Name
Geastrum
Distribution
Earthstars can be found worldwide, but are especially common in temperateTemperate refers to a climate that’s not too hot and not too cold, with moderate rainfall and distinct seasons like spring, summer, fall, and winter. You’ll find temperate areas in parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. It’s the kind of climate where you can see a wide variety of plants and animals, including deciduous trees that lose their leaves in the fall. regions.
Appearance
Their star-like appearance is their most distinguishing feature. The outer layer (peridium) splits and peels back to reveal a round spore sac. The number of “arms” and how far they recurve can vary by species.
Size
They vary in size from a few centimeters to about 12 cm across, depending on the species.
Habitat
Earthstars are typically found on the ground in woodlands, often among leaf litter or on decaying wood.
Diet
Saprotrophic, meaning they feed on decaying organic matter, especially wood.
Lifecycle
Like other fungi, Earthstars begin as spores. The spores germinate and form a network of myceliumMycelium is like the ‘root’ or the ‘body’ of a fungus. Just as plants have roots, fungi have mycelium. It is made up of tiny thread-like structures called hyphae that spread out in the soil or other materials where the fungus grows. Learn More. Under suitable conditions, this mycelium produces the puffball-like fruiting bodies. When mature, the outer layer splits, forming the characteristic star shape and revealing the spore sac. The spores are released when disturbed, starting the lifecycle anew.
Defense Mechanisms
While not particularly toxic, the tough and leathery texture of Earthstars makes them unpalatable and generally deters consumption.
Ecological Importance
They play a role in the decompositionDecomposition is a natural process that happens when living things, like plants, animals, or other organic matter, break down into simpler substances. It is a part of the circle of life and plays an essential role in recycling nutrients back into the environment. Learn More of organic material, helping in nutrient recycling within ecosystemsAn ecosystem is a community of living organisms, like insects and birds, and non-living components, like water and rocks, that interact with each other in a specific area. Learn More.
ConservationThe act of protecting and preserving natural resources and the environment. Conservation efforts are important to protect beavers and their habitats. Status
While Earthstars are generally common, specific species might be rarer than others. However, as a genus, they aren’t known to be under threat.

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.