Red Fox
Common fox, fire fox
Vulpes vulpes
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
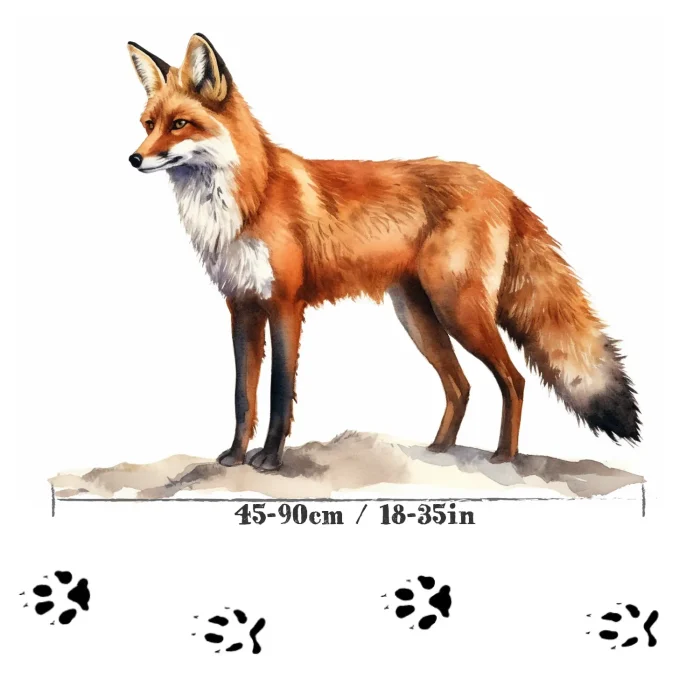
Red foxes are the largest of the true foxes and are known for their bright red coats and bushy tails. These clever animals are found all over the Northern Hemisphere and are famous for their adaptability to different environments, including forests, grasslands, mountains, and even human-altered areas. With their keen sense of hearing, they can locate small animals burrowing underground, which makes them skilled hunters. They’re curious, playful, and have a variety of vocalizations, which adds to their intriguing nature.
Red Fox

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.