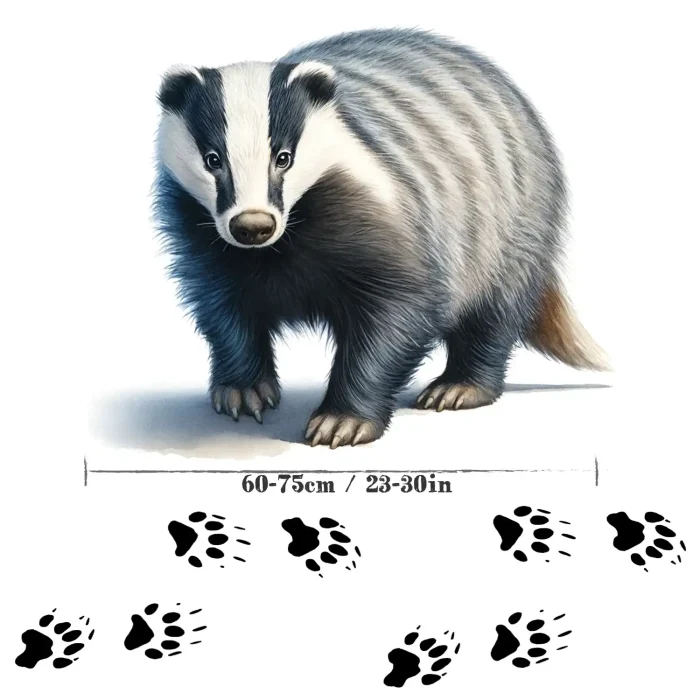
American Badger
Sand bear, Stink badger
Taxidea taxus
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
The American badger, a stocky and fierce animal, is an amazing creature often spotted across North America, from Canada to Mexico. These badgers are known for their impressive digging abilities, using their powerful claws to burrow into the ground in search of food. Not only are they outstanding diggers, but American badgers are also crucial for their ecosystemsAn ecosystem is a community of living organisms, like insects and birds, and non-living components, like water and rocks, that interact with each other in a specific area. Learn More, helping control rodent populations and even teaming up with coyotes in an unusual hunting alliance!
American Badger

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.