Appearance
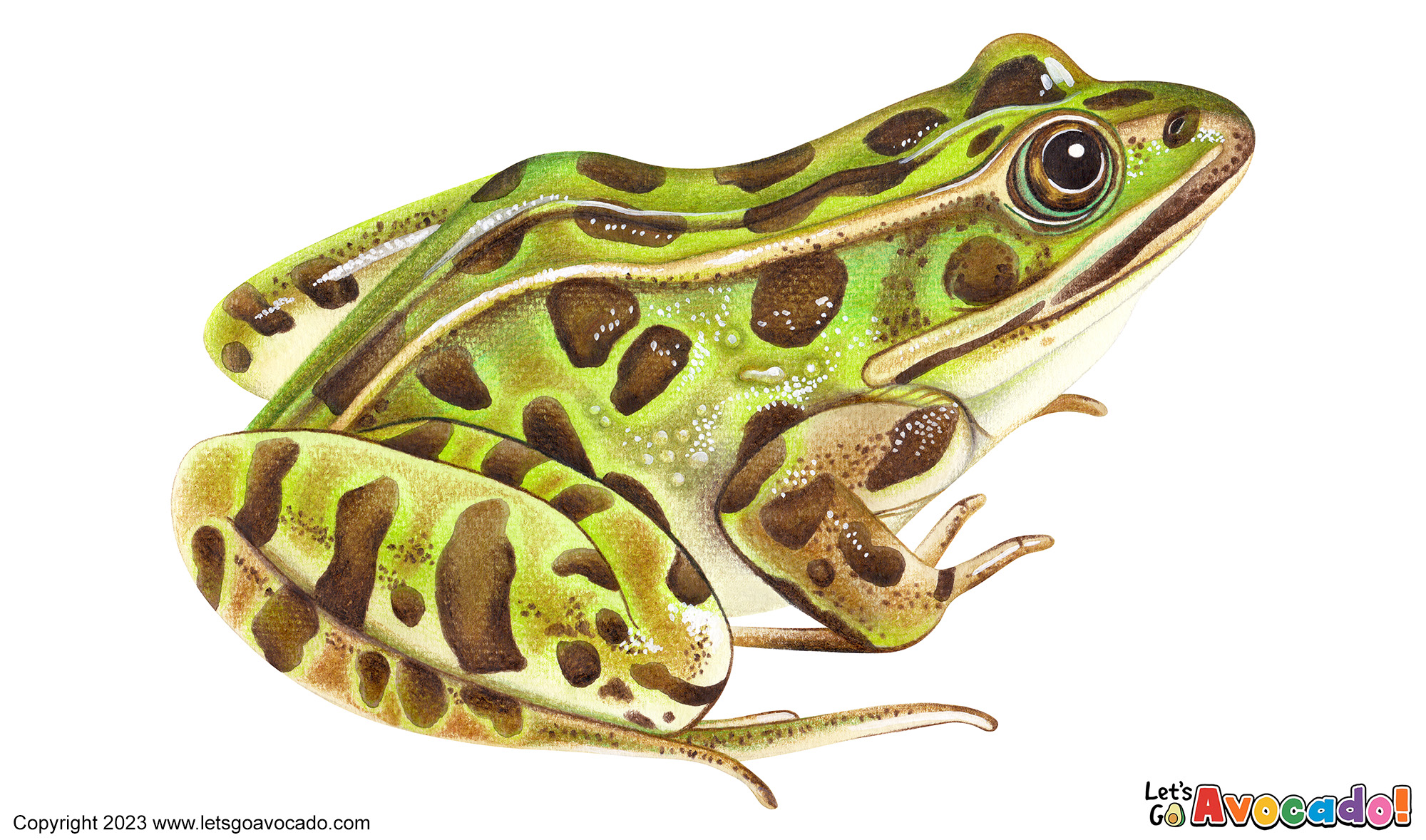
Northern leopard frogs have a distinct and eye-catching appearance. They have a green or brownish-green body with rounded spots or blotches on their skin, resembling a leopard’s pattern. The spots can be dark brown, olive, or even black. Their coloration may vary depending on their environment and can serve as camouflage.
Size
Adult northern leopard frogs typically measure around 2.4 to 4 inches (6 to 10 cm) in length. Females are generally larger than males.
Habitat
These frogs inhabit a variety of freshwater habitats, including wetlands, marshes, meadows, ponds, lakes, and slow-moving streams. They are particularly associated with areas that provide vegetation cover and suitable breeding sites, such as shallow, weedy waters.
Behavior
Northern leopard frogs are predominantly active during the night, seeking refuge in vegetation or under rocks during the day. They are known for their leaping abilities and can cover significant distances when jumping. Like most frogs, they are skilled swimmers and have long, powerful hind legs for efficient movement in water.
Vocalization
During the breeding season, male northern leopard frogs produce a series of distinctive calls to attract females. The call is often described as a repetitive, low-pitched “snore” or “rumble.” The vocal sacs of the males expand when calling, creating a resonating sound.
Diet
These frogs are opportunistic feeders and have a diet that primarily consists of invertebrates. They prey on insects, spiders, worms, small crustaceans, and occasionally, smaller frogs or tadpoles.
Lifecycle
Northern leopard frogs undergo a typical frog lifecycle, with eggs laid in water. After hatching, the tadpoles develop and undergo metamorphosis, transforming into froglets. The tadpoles have a vegetarian diet, feeding on algae and plant matter, while adult frogs are carnivorous.
Conservation Status
The northern leopard frog is considered a species of conservation concern in some regions due to habitat loss, pollution, and disease. Populations have declined in certain areas, particularly in the western part of their range. Conservation efforts focus on habitat protection, restoration, and monitoring populations to ensure their survival.