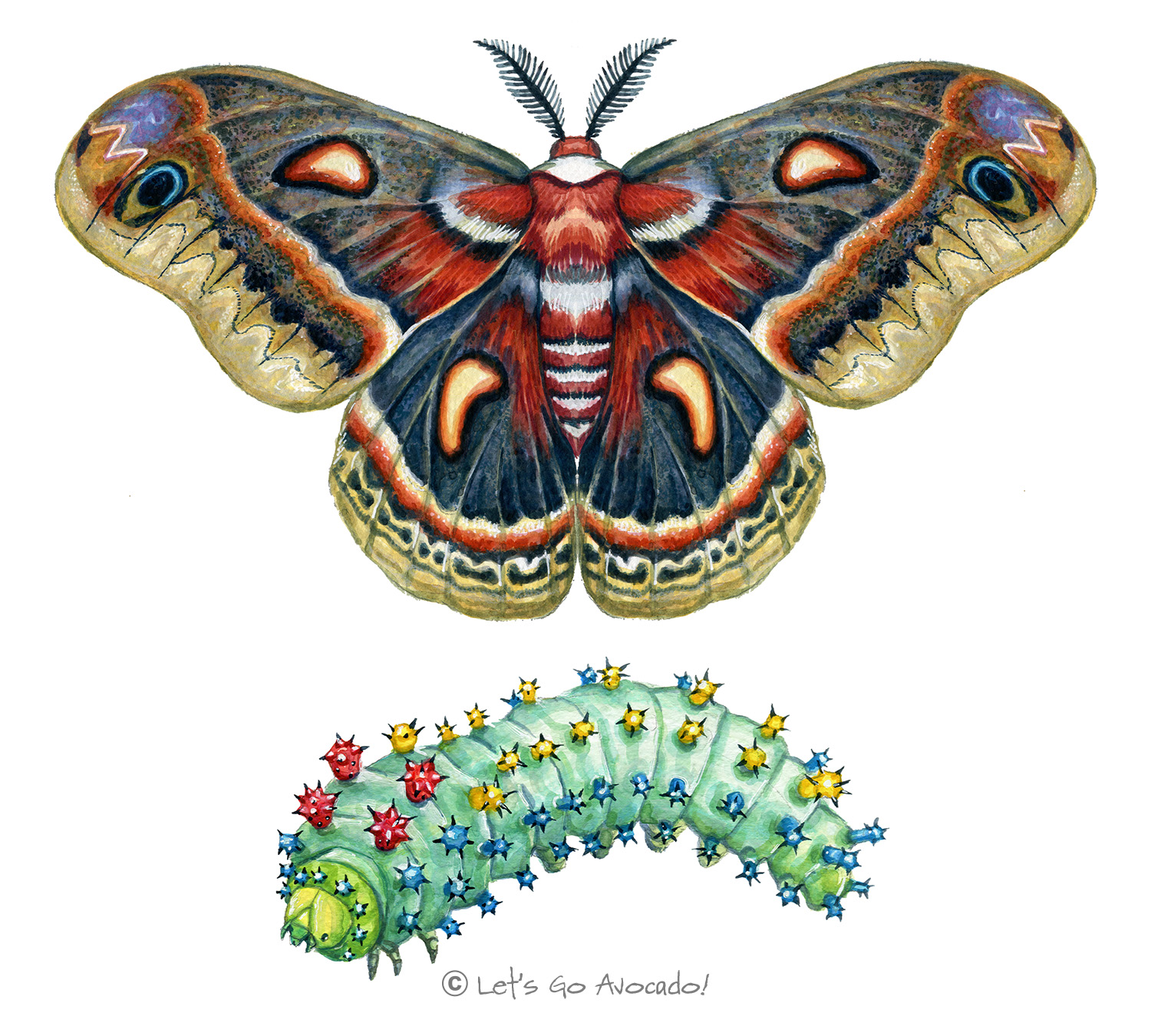
Cecropia Moth
Hyalophora cecropia
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
The Cecropia Moth is North America’s largest native moth and is celebrated for its spectacular appearance. It belongs to the Saturniidae family, a group renowned for its impressive, often large moths.
Cecropia Moth
Common Name
Cecropia Moth
Latin Name
Hyalophora cecropia
Distribution
Found across the eastern and midwestern regions of North America, from the Rocky Mountains eastward through most of the US to the maritime provinces of Canada.
Appearance
Caterpillar: The larva is bright blue-green and adorned with tubercles that have spiky, silver-colored setae.
Moth (not butterfly): The adult moth is a vivid blend of red, white, and brown with crescent-shaped white marks on the wings. The body is red with white bands, and the wings have eye-like patterns, helping deter potential predators.
Size
Moths can have a wingspan reaching 15 cm (6 inches) or more. Caterpillars can achieve lengths up to about 11 cm.
Habitat
Deciduous forests, urban gardens, and wooded suburbs.
Diet
Caterpillar: They feed on a variety of trees including maple, birch, cherry, and apple trees.
Moth: The adult Cecropia Moth does not have a functional mouth and therefore does not eat. Their adult life is solely for reproduction.
Lifecycle
Standard for moths: egg → caterpillar (larva) → cocoon (pupa, which is spun in tree branches for Cecropia) → adult moth. Adults live only for about two weeks, focused entirely on reproduction.
Communication
Cecropia Moths primarily communicate through pheromones. The female releases pheromones to attract potential male mates.
Defense Mechanisms
Caterpillar: Bright coloration can signal potential toxicity or unpalatability to predators.
Moth: The eye-like patterns on the wings serve to deter predators by either mimicking a larger animal’s eyes or by startling the predator.
Ecological Importance
They play roles as part of the food chain, serving as prey for several species, and their caterpillars help in controlling the growth of their host plants.
ConservationThe act of protecting and preserving natural resources and the environment. Conservation efforts are important to protect beavers and their habitats. Status
The Cecropia Moth is not classified as endangered or threatened, though it may face threats from habitat loss and parasitism.

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.