Canadian Tiger Swallowtail
Papilio canadensis
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
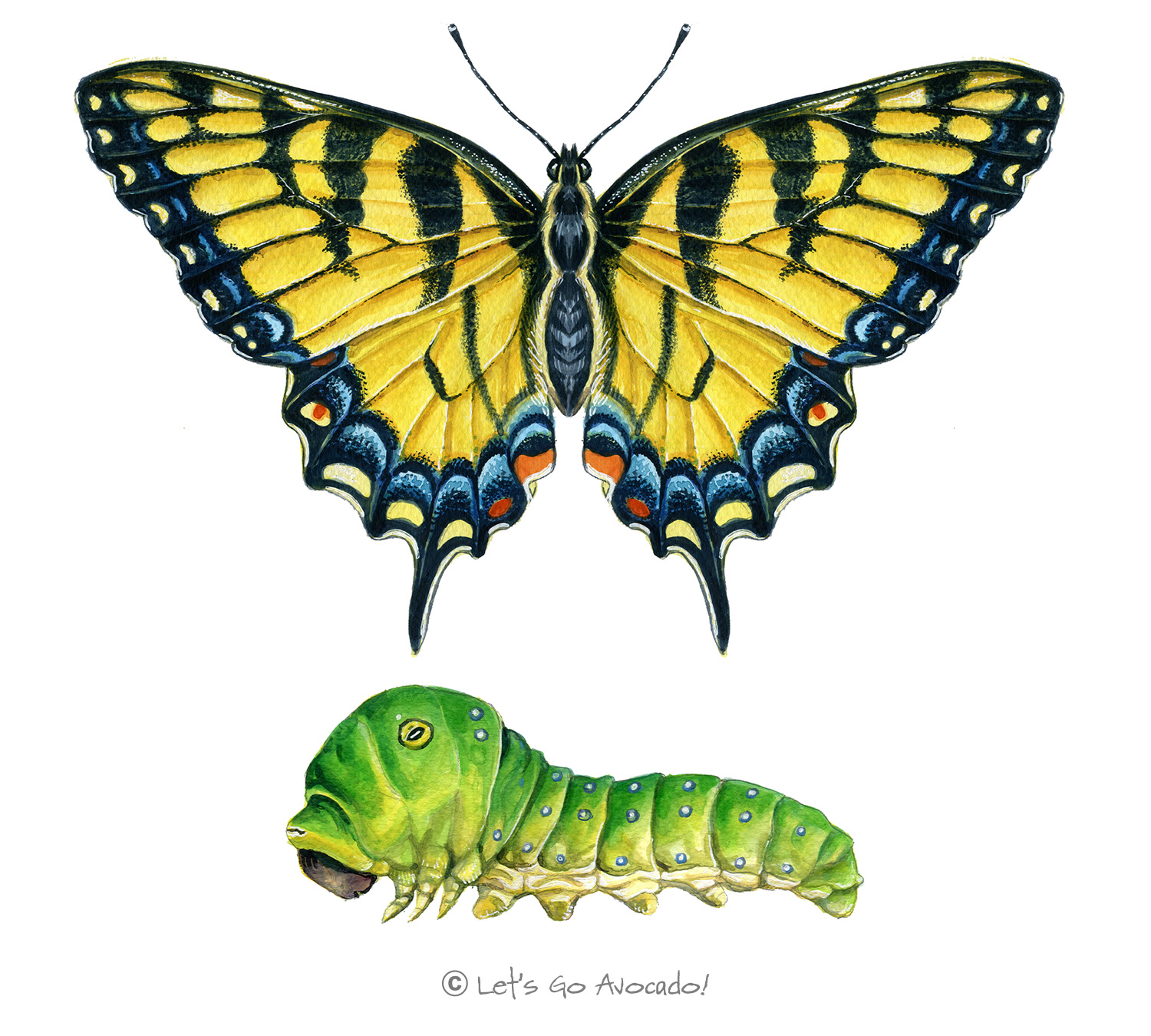
The Canadian Tiger Swallowtail is a beautiful, large butterfly with bold black and yellow stripes, typical of the ‘tiger’ swallowtails. This butterfly graces many northern areas and is a delight to see fluttering in the summer sun.
Canadian Tiger Swallowtail
Common Name
Canadian Tiger Swallowtail
Latin Name
Papilio canadensis
Distribution
Found throughout Canada, from the northern parts of the Great Lakes, across the boreal forest to Alaska, and extending into the northern regions of the US, particularly in the Rocky Mountains.
Appearance
Caterpillar: They are initially brown and white, resembling bird droppings, but as they grow, they turn green with a pair of yellow eyespots with black and blue centers on the thorax.
Butterfly: It has yellow wings with black tiger striping. There’s a splash of blue and orange near the tail of the hindwing.
Size
Wingspan ranges from 7 to 10 cm. Caterpillars can grow up to 5 cm in length.
Habitat
Various open and wooded areas, especially in more northern latitudes and higher elevations. Common habitats include woodlands, fields, riversides, and suburban areas.
Diet
Caterpillar: They feed on leaves of various trees including aspen, willow, and birch.
Butterfly: Prefers nectar from flowers such as dandelion, lilac, and chokecherry.
Lifecycle
Egg → caterpillar (larva) → chrysalis (pupa) → adult butterfly. After mating, females lay single green eggs on the leaves of host plants. Caterpillars emerge, eat, and grow, eventually pupating into a chrysalis from which the adult butterfly emerges.
Communication
Like other butterflies, the Canadian Tiger Swallowtail primarily communicates through visual cues and chemical signals, particularly pheromones during mating rituals.
Defense Mechanisms
Caterpillar: The eyespots on the caterpillar deter predators by mimicking the eyes of larger animals. The early instars resemble bird droppings, providing camouflage.
Butterfly: Their bright colors may signal potential distastefulness to predators. The tail-like extensions on the hindwings can also divert attacks away from vital body areas.
Ecological Importance
Pollination is a significant role, helping in the reproduction of many plants. As a prey species, they’re crucial for the food chain, feeding birds and other predators.
ConservationThe act of protecting and preserving natural resources and the environment. Conservation efforts are important to protect beavers and their habitats. Status
It’s not considered endangered or threatened and is common in its range.

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.