Texas Cuckoo Leafcutter Bee
Texas cuckoo bee, Cuckoo leafcutter bee
Coelioxys texana
This page may contain affiliate links.
Read our disclosure and privacy policy here.
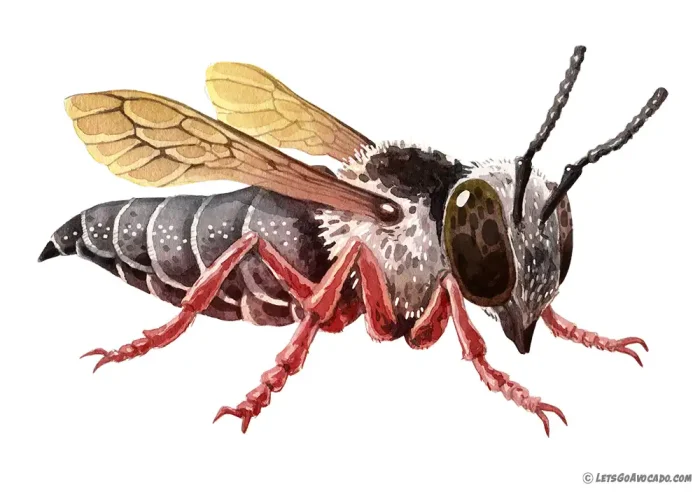
The Texas cuckoo leafcutter bee is an intriguing insect known for its unique parasitic lifestyle. These bees do not build their own nests but instead lay their eggs in the nests of other leafcutter bees. This sneaky behavior is why they are called “cuckoo” bees, named after the cuckoo bird, which lays its eggs in the nests of other birds. The Texas cuckoo leafcutter bee is found mainly in North America, where it inhabits areas with plenty of flowering plants.
What makes the Texas cuckoo leafcutter bee fascinating is its appearance and behavior. These bees have a shiny, metallic body and are often smaller than their host bees. Unlike most bees, they do not collect pollen for their young. Instead, their larvae feed on the provisions left by the host bee. Despite their sneaky behavior, they play an important role in the ecosystem by keeping other bee populations in check and contributing to pollination.
Texas Cuckoo Leafcutter Bee

There’s a lot to explore right where we are, in our own neighborhoods and backyards! Join us while we get off the couch and explore the everyday wonders of nature, science, space, engineering, art, and anything else we stumble upon during on our adventures.